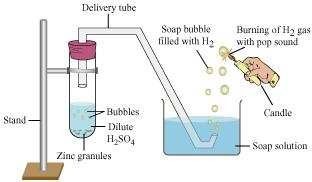
धातुएं और अधातुएं
अभ्यास प्रश्न सेट 1
प्रश्न 1: एक धातु का उदाहरण दीजिए जो:
- (i) कमरे के तापमान पर तरल होती है।
- (ii) चाकू से आसानी से काटी जा सकती है।
- (iii) गर्मी का सबसे अच्छा चालक है।
- (iv) गर्मी का एक गरीब चालक है।
उत्तर:
- (i) धातु जो कमरे के तापमान पर तरल होती है → पारा
- (ii) धातु जिसे चाकू से आसानी से काटा जा सकता है → सोडियम
- (iii) धातु जो गर्मी का सबसे अच्छा चालक है → चांदी
- (iv) धातु जो गर्मी का गरीब चालक है → पारा और सीसा
प्रश्न 2: “मैलियाबल” और “डक्टाइल” का अर्थ समझाइए।
उत्तर:
- मैलियाबल: वे पदार्थ जो पतली चादरों में दबाए जा सकते हैं, उन्हें मैलियाबल कहा जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, अधिकांश धातुएं मैलियाबल होती हैं।
- डक्टाइल: वे पदार्थ जो पतली तारों में खींचे जा सकते हैं, उन्हें डक्टाइल कहा जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, अधिकांश धातुएं डक्टाइल होती हैं।
अभ्यास प्रश्न सेट 2
प्रश्न 1: निम्नलिखित शब्दों को परिभाषित कीजिए।
(i) खनिज(ii) अयस्क
(iii) गैंगू
उत्तर:
(i) खनिज: अधिकांश तत्व प्रकृति में संयुक्त रूप में खनिजों के रूप में पाए जाते हैं। खनिजों का रासायनिक संघटन निश्चित होता है।
(ii) अयस्क: वे खनिज जिनसे धातु को लाभकारी रूप से निकाला जा सकता है, उन्हें अयस्क कहा जाता है।
(iii) गैंगू: अयस्क में उपस्थित अशुद्धियाँ (बालू, कीचड़, मिट्टी, कंकड़ आदि) गैंगू कहलाती हैं।
प्रश्न 2: निम्नलिखित प्रतिक्रियाओं के समीकरण लिखिए:
(i) लोहे का भाप के साथ प्रतिक्रिया(ii) कैल्शियम और पोटेशियम का पानी के साथ प्रतिक्रिया
उत्तर:
(i) लोहे का भाप के साथ प्रतिक्रिया:
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(ii) कैल्शियम और पोटेशियम का पानी के साथ प्रतिक्रिया:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
प्रश्न 3: चार धातुओं A, B, C, और D के नमूने लिए गए और उन्हें निम्नलिखित समाधान में एक-एक करके डाला गया। प्राप्त परिणामों का सारांश नीचे दिया गया है।
| धातु | आयरन (II) सल्फेट | कॉपर (II) सल्फेट | जिंक सल्फेट | सिल्वर नाइट्रेट |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | स्थानांतरण | ||
| B. | स्थानांतरण | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | ||
| C. | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | स्थानांतरण |
| D. | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं |
उपरोक्त तालिका का उपयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों का उत्तर दीजिए।
(i) सबसे प्रतिक्रियाशील धातु कौन सी है?
(ii) यदि B को कॉपर (II) सल्फेट के समाधान में डाला जाए तो क्या देखेंगे?
(iii) धातु A, B, C, और D को घटते हुए प्रतिक्रियाशीलता के क्रम में कैसे व्यवस्थित करेंगे?
उत्तर:
व्याख्या:
A + FeSO4: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् A लोहे से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
A + CuSO4: स्थानांतरण, अर्थात् A कॉपर से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
B + FeSO4: स्थानांतरण, अर्थात् B लोहे से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
B + ZnSO4: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् B जिंक से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
C + FeSO4: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् C लोहे से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
C + CuSO4: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् C कॉपर से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
C + ZnSO4: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् C जिंक से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
C + AgNO3: स्थानांतरण, अर्थात् C चांदी से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
D + FeSO4/CuSO4/ZnSO4/AgNO3: कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं, अर्थात् D लोहे, कॉपर, जिंक, और चांदी से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।

(i) B सबसे प्रतिक्रियाशील धातु है।
(ii) यदि B को कॉपर (II) सल्फेट के समाधान में डाला जाए, तो यह कॉपर को स्थानांतरित कर देगा।
B + CuSO4 → स्थानांतरण
(iii) धातुओं का घटते हुए प्रतिक्रियाशीलता के क्रम में संयोजन इस प्रकार है: B > A > C > D
प्रश्न 4: जब एक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातु को पतला हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल में डाला जाता है, तो कौन सा गैस उत्पन्न होता है? जब लोहे की प्रतिक्रिया पतले H2SO4 के साथ होती है, तो रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया क्या होती है?
उत्तर:
जब पतला हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल एक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातु में डाला जाता है, तो हाइड्रोजन गैस उत्पन्न होती है। जब लोहे की प्रतिक्रिया पतले H2SO4 के साथ होती है, तो लोहे (II) सल्फेट के साथ हाइड्रोजन गैस उत्पन्न होती है।
Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
प्रश्न 5: जब जिंक को आयरन (II) सल्फेट के समाधान में डाला जाता है, तो आप क्या देखेंगे? जो रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया होती है, वह लिखिए।
उत्तर:
जिंक लोहे से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है। इसलिए, जब जिंक को आयरन (II) सल्फेट के समाधान में डाला जाएगा, तो यह लोहे को स्थानांतरित कर देगा।
Zn + FeSO4 → ZnSO4 + Fe
अभ्यास प्रश्न सेट 3
प्रश्न 1:
(i) सोडियम, ऑक्सीजन और मैग्नीशियम के इलेक्ट्रॉन-डॉट संरचनाएँ लिखिए।
उत्तर:
उपस्थित तत्वों के वैलेंस इलेक्ट्रॉनों को डॉट्स के रूप में प्रदर्शित करने को इलेक्ट्रॉन-डॉट संरचना कहा जाता है।

(ii) Na2O और MgO के निर्माण को इलेक्ट्रॉनों के स्थानांतरण द्वारा दिखाइए।
उत्तर:
Na2O के निर्माण के लिए इलेक्ट्रॉन स्थानांतरण:
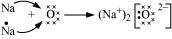
2Na → 2Na+ + 2e- (सोडियम इलेक्ट्रॉन खोता है) O + 2e- → O2- (ऑक्सीजन इलेक्ट्रॉन प्राप्त करता है) Na+ + O2- → Na2O
MgO के निर्माण के लिए इलेक्ट्रॉन स्थानांतरण:
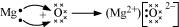
Mg → Mg2+ + 2e- (मैग्नीशियम इलेक्ट्रॉन खोता है) O + 2e- → O2- (ऑक्सीजन इलेक्ट्रॉन प्राप्त करता है) Mg2+ + O2- → MgO
(iii) इन यौगिकों में कौन से आयन उपस्थित हैं?
उत्तर:
Na2O में Na+ और O2- आयन उपस्थित हैं, और MgO में Mg2+ और O2- आयन उपस्थित हैं।
प्रश्न 2: दो धातुओं का नाम बताइए जो प्रकृति में मुक्त अवस्था में पाई जाती हैं।
उत्तर:
प्रतिक्रियाशीलता श्रेणी के नीचे की धातुएं मुख्य रूप से मुक्त अवस्था में पाई जाती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए: सोना, चांदी, और प्लेटिनम।
प्रश्न 3: धातु को उसके ऑक्साइड से प्राप्त करने के लिए कौन सी रासायनिक प्रक्रिया का उपयोग किया जाता है?
उत्तर:
धातु को उसके ऑक्साइड से प्राप्त करने के लिए रिडक्शन (अवकरण) प्रक्रिया का उपयोग किया जाता है। इस प्रक्रिया में धातु के ऑक्साइड को उचित रिड्यूसिंग एजेंट्स जैसे कार्बन या अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातुओं के द्वारा रिड्यूस किया जाता है, ताकि धातु को उसके ऑक्साइड से विस्थापित किया जा सके।
उदाहरण के लिए, जिंक ऑक्साइड को कार्बन के साथ गर्म करके धातु जिंक में परिवर्तित किया जाता है।
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
मैंगनीज डाइऑक्साइड को अल्युमिनियम पाउडर के साथ उपचारित करके मैंगनीज में रिड्यूस किया जाता है। इस प्रक्रिया में, अल्युमिनियम मैंगनीज को उसके ऑक्साइड से विस्थापित करता है:
MnO2 (s) + 2Al (s) → 2Al3+ (aq) + Mn (s) + heat
अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातुओं के ऑक्साइड्स को रिड्यूस करने के लिए इलेक्ट्रोलिसिस की प्रक्रिया का उपयोग किया जाता है।
अभ्यास प्रश्न सेट 4
प्रश्न 1: जिंक, मैग्नीशियम और तांबे के धातु ऑक्साइड को निम्नलिखित धातुओं के साथ गर्म किया गया।
| धातु | जिंक | मैग्नीशियम | तांबा |
|---|---|---|---|
| जिंक ऑक्साइड | – | – | – |
| मैग्नीशियम ऑक्साइड | – | – | – |
| तांबा ऑक्साइड | – | – | – |
उत्तर:
| धातु | जिंक | मैग्नीशियम | तांबा |
|---|---|---|---|
| जिंक ऑक्साइड | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | प्रतिस्थापन | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं |
| मैग्नीशियम ऑक्साइड | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं |
| तांबा ऑक्साइड | प्रतिस्थापन | प्रतिस्थापन | कोई प्रतिक्रिया नहीं |
प्रश्न 2: कौन सी धातुएं आसानी से जंग नहीं लगतीं?
उत्तर:
जो धातु अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील होती है, वह अधिक संभावना से जंग लगती है। इसलिए, कम प्रतिक्रियाशील धातुएं कम जंग लगती हैं। यही कारण है कि सोने की परत जंग से उच्च प्रतिरोध प्रदान करती है।
प्रश्न 3: मिश्रधातु (Alloys) क्या होते हैं?
उत्तर:
मिश्रधातुएं दो या दो से अधिक तत्वों का समरूप मिश्रण होती हैं। ये तत्व दो धातुएं हो सकती हैं, या एक धातु और एक अधातु हो सकती है। एक मिश्रधातु तब बनती है जब धातु को पहले पिघलाया जाता है और फिर उसमें अन्य तत्वों को घोला जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, स्टील लोहे और कार्बन की मिश्रधातु है।
अभ्यास प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1: निम्नलिखित जोड़ों में से कौन से प्रतिस्थापन प्रतिक्रियाएँ उत्पन्न करेंगे?
- (a) NaCl घोल और तांबा धातु
- (b) MgCl2 घोल और एल्यूमिनियम धातु
- (c) FeSO4 घोल और चांदी धातु
- (d) AgNO3 घोल और तांबा धातु
उत्तर:
(d) AgNO3 घोल और तांबा धातु
प्रश्न 2: निम्नलिखित विधियों में से कौन सी लोहे के फ्राईंग पैन को जंग लगने से रोकने के लिए उपयुक्त है?
- (a) चिकनाई लगाना
- (b) पेंट लगाना
- (c) जिंक की परत लगाना
- (d) ऊपर के सभी
उत्तर:
(c) जिंक की परत लगाना
(हम चिकनाई और पेंट भी लगा सकते हैं ताकि लोहे को जंग से बचाया जा सके। हालांकि, एक लोहे के फ्राईंग पैन के मामले में, चिकनाई और पेंट का उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता क्योंकि जब पैन को गर्म किया जाता है और बार-बार धोया जाता है, तो चिकनाई और पेंट की परत नष्ट हो जाएगी।)
प्रश्न 3: एक तत्व ऑक्सीजन के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करता है और एक यौगिक बनाता है जिसका उच्च गलनांक होता है। यह यौगिक पानी में भी घुलनशील है। यह तत्व संभवतः कौन सा हो सकता है?
- (a) कैल्शियम
- (b) कार्बन
- (c) सिलिकॉन
- (d) लोहा
उत्तर:
(a) यह तत्व संभवतः कैल्शियम हो सकता है।
प्रश्न 4: खाद्य कनस्तरों को जिंक की बजाय टिन से क्यों कोट किया जाता है?
- (a) जिंक टिन से महंगा है।
- (b) जिंक का गलनांक टिन से अधिक है।
- (c) जिंक टिन से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
- (d) जिंक टिन से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
उत्तर:
(c) खाद्य कनस्तरों को जिंक की बजाय टिन से कोट किया जाता है क्योंकि जिंक टिन से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील है।
प्रश्न 5: आपको एक हथौड़ा, बैटरी, बल्ब, तार और स्विच दिए गए हैं।
(a) आप इनका उपयोग करके धातुओं और अधातुओं के नमूनों के बीच अंतर कैसे कर सकते हैं?
(b) इन परीक्षणों की धातुओं और अधातुओं के बीच अंतर करने में उपयोगिता का मूल्यांकन करें।
उत्तर:
(a) हथौड़े से हम नमूने को मार सकते हैं, और यदि यह पतली चादरों में मुरझा सकता है (यानी यह कूटनीय है), तो यह एक धातु है; अन्यथा, यह एक अधातु है। इसी तरह, बैटरी, बल्ब, तार और स्विच का उपयोग करके हम एक सर्किट बना सकते हैं। यदि नमूना विद्युत प्रवाह का संचालन करता है, तो यह एक धातु है; अन्यथा, यह एक अधातु है।
(b) उपरोक्त परीक्षण धातुओं और अधातुओं के बीच अंतर करने में उपयोगी हैं क्योंकि ये भौतिक गुणों पर आधारित होते हैं। इन परीक्षणों में कोई रासायनिक प्रतिक्रियाएँ शामिल नहीं हैं।
प्रश्न 6: एंफोटेरिक ऑक्साइड क्या होते हैं? एंफोटेरिक ऑक्साइड के दो उदाहरण दें।
उत्तर:
वे ऑक्साइड जो दोनों अम्लीय और क्षारीय ऑक्साइड के रूप में व्यवहार करते हैं, उन्हें एंफोटेरिक ऑक्साइड कहा जाता है। उदाहरण: एल्युमिनियम ऑक्साइड (Al2O3), जिंक ऑक्साइड (ZnO)
प्रश्न 7: उन दो धातुओं का नाम बताइए जो पतला अम्ल से हाइड्रोजन विस्थापित करती हैं, और उन दो धातुओं का नाम बताइए जो ऐसा नहीं करतीं।
उत्तर:
जो धातुएं हाइड्रोजन से अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील होती हैं, वे इसे पतले अम्लों से विस्थापित करती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए: सोडियम और पोटेशियम। जो धातुएं हाइड्रोजन से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील होती हैं, वे इसे विस्थापित नहीं करतीं। उदाहरण के लिए: तांबा और चांदी।
प्रश्न 8: धातु M के विद्युत परिष्करण में, आप एनोड, कैथोड और इलेक्ट्रोलाइट के रूप में क्या लेंगे?
उत्तर:
धातु M के विद्युत परिष्करण में:
- एनोड → अशुद्ध धातु M
- कैथोड → शुद्ध धातु M की पतली पट्टी
- इलेक्ट्रोलाइट → धातु M के लवण का घोल
प्रश्न 9: प्रत्युष ने एक पट्टी पर सल्फर पाउडर लिया और उसे गर्म किया। उसने उत्पन्न गैस को एक परीक्षण ट्यूब को इसके ऊपर उल्टा करके इकट्ठा किया, जैसा कि नीचे चित्रित किया गया है।
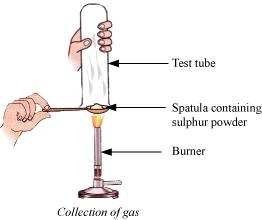
(a) गैस का इन पर क्या प्रभाव होगा:
- (i) सूखी लिटमस कागज पर?
- (ii) गीली लिटमस कागज पर?
उत्तर:
(a) (i) सूखी लिटमस कागज पर इसका कोई प्रभाव नहीं होगा।
(ii) चूंकि गैस सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड (SO2) है, यह गीली नीली लिटमस कागज को लाल कर देती है, क्योंकि सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड नमी के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करके सल्फ्यूरस एसिड बनाता है।
(b) हो रही प्रतिक्रिया के लिए संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण लिखें:
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
SO2 (g) + H2O (l) → H2SO3 (aq)
प्रश्न 10: लोहे के जंग को रोकने के दो तरीके बताइए।
उत्तर:
- (i) तेल, ग्रीस, या पेंट लगाना: तेल, ग्रीस, या पेंट लगाने से सतह जलरोधक हो जाती है और वायुमंडल में मौजूद नमी और ऑक्सीजन से लोहे का संपर्क नहीं हो पाता। इस प्रकार जंग लगने से बचाव होता है।
- (ii) गैल्वनाइजेशन: एक लोहे की वस्तु को जिंक धातु की परत से कोट किया जाता है, जो लोहे को ऑक्सीजन और नमी से संपर्क करने से रोकता है। इस प्रकार जंग लगने से बचाव होता है।
प्रश्न 11: जब गैर-धातुएं ऑक्सीजन से मिलती हैं, तो कौन सी प्रकार की ऑक्साइड बनती हैं?
उत्तर:
गैर-धातुएं ऑक्सीजन से मिलकर अम्लीय ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए:
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
प्रश्न 12: कारण बताइए:
- (a) प्लेटिनम, सोना, और चांदी का उपयोग गहनों के रूप में क्यों किया जाता है?
- (b) सोडियम, पोटैशियम और लिथियम को तेल में क्यों रखा जाता है?
- (c) एल्यूमिनियम एक अत्यधिक प्रतिक्रिया करने वाली धातु है, फिर भी इसका उपयोग रसोई के बर्तनों को बनाने में क्यों किया जाता है?
- (d) कार्बोनेट और सल्फाइड अयस्कों को आमतौर पर निष्कर्षण प्रक्रिया के दौरान ऑक्साइड में क्यों बदला जाता है?
उत्तर:
(a) प्लेटिनम, सोना, और चांदी का उपयोग गहनों के रूप में किया जाता है क्योंकि ये बहुत चमकदार होते हैं। साथ ही, ये बहुत कम प्रतिक्रियाशील होते हैं और आसानी से जंग नहीं लगते।
(b) सोडियम, पोटैशियम और लिथियम अत्यधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातुएं हैं और ये हवा और पानी के साथ तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया करते हैं। इसलिए, इनको हवा और नमी से बचाने के लिए तेल में रखा जाता है।
(c) हालांकि एल्यूमिनियम एक अत्यधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातु है, यह संक्षारण के लिए प्रतिरोधी है। इसका कारण यह है कि एल्यूमिनियम हवा में मौजूद ऑक्सीजन से प्रतिक्रिया करके एक पतली परत एल्यूमिनियम ऑक्साइड बना लेता है। यह ऑक्साइड परत बहुत स्थिर होती है और एल्यूमिनियम को और प्रतिक्रिया करने से रोकती है। इसके अलावा, यह हल्का और गर्मी का अच्छा चालक होता है। इसलिए इसका उपयोग रसोई के बर्तनों के निर्माण में किया जाता है।
(d) कार्बोनेट और सल्फाइड अयस्कों को आमतौर पर ऑक्साइड में बदला जाता है क्योंकि धातुओं को उनके ऑक्साइड से निकालना कार्बोनेट और सल्फाइड से निकालने से आसान होता है।
प्रश्न 13: आपने देखा होगा कि ताम्बे के बर्तनों को नींबू या इमली के रस से साफ किया जाता है। समझाइए कि ये खट्टे पदार्थ बर्तनों को साफ करने में क्यों प्रभावी होते हैं।
उत्तर:
ताम्बा हवा में नमी के साथ मिलकर ताम्बा कार्बोनेट बनाता है और इसके परिणामस्वरूप ताम्बा बर्तन अपनी चमकदार भूरी सतह को खोकर ताम्बा कार्बोनेट की हरी परत बना लेते हैं। नींबू या इमली में उपस्थित साइट्रिक एसिड ताम्बा कार्बोनेट को न्यूट्रल कर देता है और उसकी परत को घोल देता है। यही कारण है कि ताम्बे के बर्तनों को नींबू या इमली के रस से साफ किया जाता है, जिससे ताम्बे के बर्तन की विशिष्ट चमक फिर से आ जाती है।
प्रश्न 14: धातु और गैर-धातु के बीच उनके रासायनिक गुणों के आधार पर अंतर बताइए।
उत्तर:
| धातु | गैर-धातु |
|---|---|
| धातु विद्युत सकारात्मक होते हैं। | गैर-धातु विद्युत नकारात्मक होते हैं। |
| वे ऑक्सीजन से मिलकर क्षारीय ऑक्साइड बनाते हैं। | वे ऑक्सीजन से मिलकर अम्लीय या न्यूट्रल ऑक्साइड बनाते हैं। |
| वे पानी से प्रतिक्रिया करके ऑक्साइड और हाइड्रॉक्साइड बनाते हैं। कुछ धातुएं ठंडे पानी से, कुछ गर्म पानी से और कुछ भाप से प्रतिक्रिया करती हैं। | वे पानी के साथ प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करते। |
| वे पतला अम्लों के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करके नमक और हाइड्रोजन गैस उत्पन्न करते हैं। हालांकि, Cu, Ag, Au, Pt, Hg प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करते। | वे पतला अम्लों के साथ प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करते। ये हाइड्रोजन को प्रतिस्थापित करने में सक्षम नहीं होते। |
| वे धातुओं के नमक घोल के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करते हैं। उनकी प्रतिक्रियाशीलता के आधार पर विस्थापन प्रतिक्रिया हो सकती है। | वे गैर-धातुओं के नमक घोल के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करते हैं। |
| वे reduक्शन एजेंट के रूप में कार्य करते हैं (क्योंकि वे आसानी से इलेक्ट्रॉन खो सकते हैं)। | वे ऑक्सीकरण एजेंट के रूप में कार्य करते हैं (क्योंकि वे इलेक्ट्रॉन प्राप्त कर सकते हैं)। |
प्रश्न 15: एक व्यक्ति सोने का आभूषण बेचने का नाटक करते हुए घर-घर गया। उसने पुराने और धुंधले सोने के आभूषणों को फिर से चमकाने का वादा किया। एक बेखबर महिला ने उसे सोने के कंगन का एक सेट दिया जिसे उसने एक विशेष घोल में डुबो दिया। कंगन नए जैसे चमकने लगे, लेकिन उनका वजन बहुत कम हो गया। महिला दुखी हो गई, लेकिन एक निरर्थक तर्क के बाद व्यक्ति जल्दी से भाग गया। क्या आप जासूस की तरह अनुमान लगा सकते हैं कि उसने जो घोल इस्तेमाल किया था, वह किस प्रकार का था?
उत्तर:
उसने सोने को एक घोल में डुबोया होगा जिसे ‘आक्वा रेगिया’ कहा जाता है − यह एक 3:1 मिश्रण होता है सांद्र HCl और सांद्र HNO3 का। आक्वा रेगिया एक धुंआधार, अत्यधिक संक्षारक तरल होता है। यह सोने को घोलता है। जब सोने के आभूषणों को आक्वा रेगिया में डुबोया जाता है, तो सोने की बाहरी परत घुल जाती है और अंदर की चमचमाती परत प्रकट हो जाती है। इस कारण सोने के आभूषणों का वजन कम हो जाता है।
प्रश्न 16: ताम्बे का उपयोग गरम पानी के टैंक बनाने के लिए क्यों किया जाता है और स्टील (लोहा का मिश्र धातु) से नहीं?
उत्तर:
ताम्बा ठंडे पानी, गरम पानी, या भाप से प्रतिक्रिया नहीं करता। लेकिन लोहे में भाप के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करने की प्रवृत्ति होती है। यदि गरम पानी के टैंक स्टील (लोहे के मिश्र धातु) से बनाए जाते, तो लोहे की भाप के साथ तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया होती। इस कारण ताम्बे का उपयोग गरम पानी के टैंक बनाने के लिए किया जाता है, स्टील का नहीं।
प्रश्न 17: सोडियम को केरोसिन तेल में क्यों रखा जाता है?
उत्तर:
सोडियम और पोटैशियम अत्यधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील धातुएं हैं और ये हवा के साथ और पानी के साथ विस्फोटक प्रतिक्रिया करती हैं। इस कारण इन्हें खुला रखने पर ये आग पकड़ सकती हैं। इसलिए, इनसे दुर्घटनाओं को रोकने के लिए सोडियम को केरोसिन तेल में रखा जाता है।
प्रश्न 18: आयनिक यौगिकों का पिघलने का बिंदु ऊंचा क्यों होता है?
उत्तर:
आयनिक यौगिकों में आयनों के बीच मजबूत विद्युत-आकर्षण बल होते हैं। इसलिये इन बलों को पार करने के लिए बहुत अधिक ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है। इस कारण आयनिक यौगिकों का पिघलने का बिंदु ऊंचा होता है।